CFC Week 9: Incident Management
Learning outcomes
- Explain the Incident Management process.
- List the elements of the logging process.
- Describe the life cycle of events.
What is the incident?
is an unexpected event that disrupts the normal operation of a system
What is the objective of the incident management process?
is to return the service to normal operation as quickly as possbile after disruption
What is the aim of incident management process?
create as little negative impact as possbile on the business
What are two modes of operations in incident management process?
-
In practice : find a temporal workaround to ensure services are up and running
-
In parallel : - investigate the incident
- identify the cause root
- find a permanent fix
What are frameworks used to tackle incidents?
- ITIL
- Information technology infrastructure library
- uses a workflow for efficient resolution
What are incident management workflow?
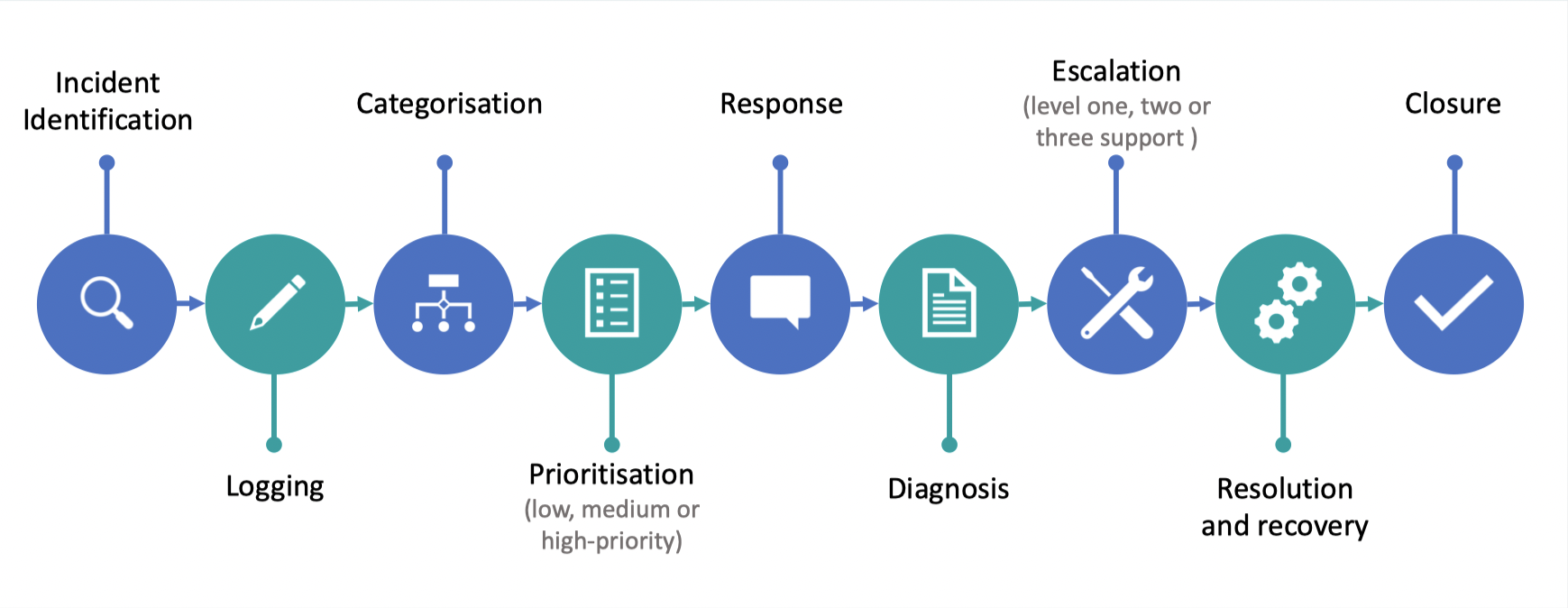
- Incident management
- Logging
Streamlined processes
- Categorisation
- Prioritisation
- Response
Follow corporations’ guidelines
-
Diagnosis
-
Escalation
-
Resolution and recovery
-
closure
What is Incident identification in incident management workflow?
Incidents are generally reported when attacks or incidents have been identified
- Unreported incidents
- False negative, pose a systematic risk to the organisation
- Mistakenly reported incidents
- False positives, when the system begin to report anomalous behaviours?
Where does incident identification start with?
It start with identify through the automated/manual analysis of digital artefacts and logs
What is logging process in incident management workflow?
- Logging is the process in which systems and applications inform about “what they do.”
- Useful to administrators to check when something goes wrong
Does incident management workflow always start with analysis of digital artefacts and logs?
Incidents are often discovered by the user of the system
- they notice that something is abnormal
- they simply see evidence of an attack
What are the most important elements of the logging process?
The most important one is the event.
- Event
- a single occurrence within an environment
- consists of event fields and event records
- event fields describe characteristic of the event
- event records describe a collection of event fields
What is Log in logging process?
- Log
- a collection of event records
- data logs
- log files
What is Audit in logging process?
- Audit
- process of evaluating logs
What is Recording in logging process?
- Recording
- Process of tracking event fields (“I am going to track an IP address”)
What is Logging in logging process
- Logging
- is the process of saving events into logs
What is Security incident in logging process
- Security incident
- is the occurrence of a security event (intrusion attempt or data leakage)
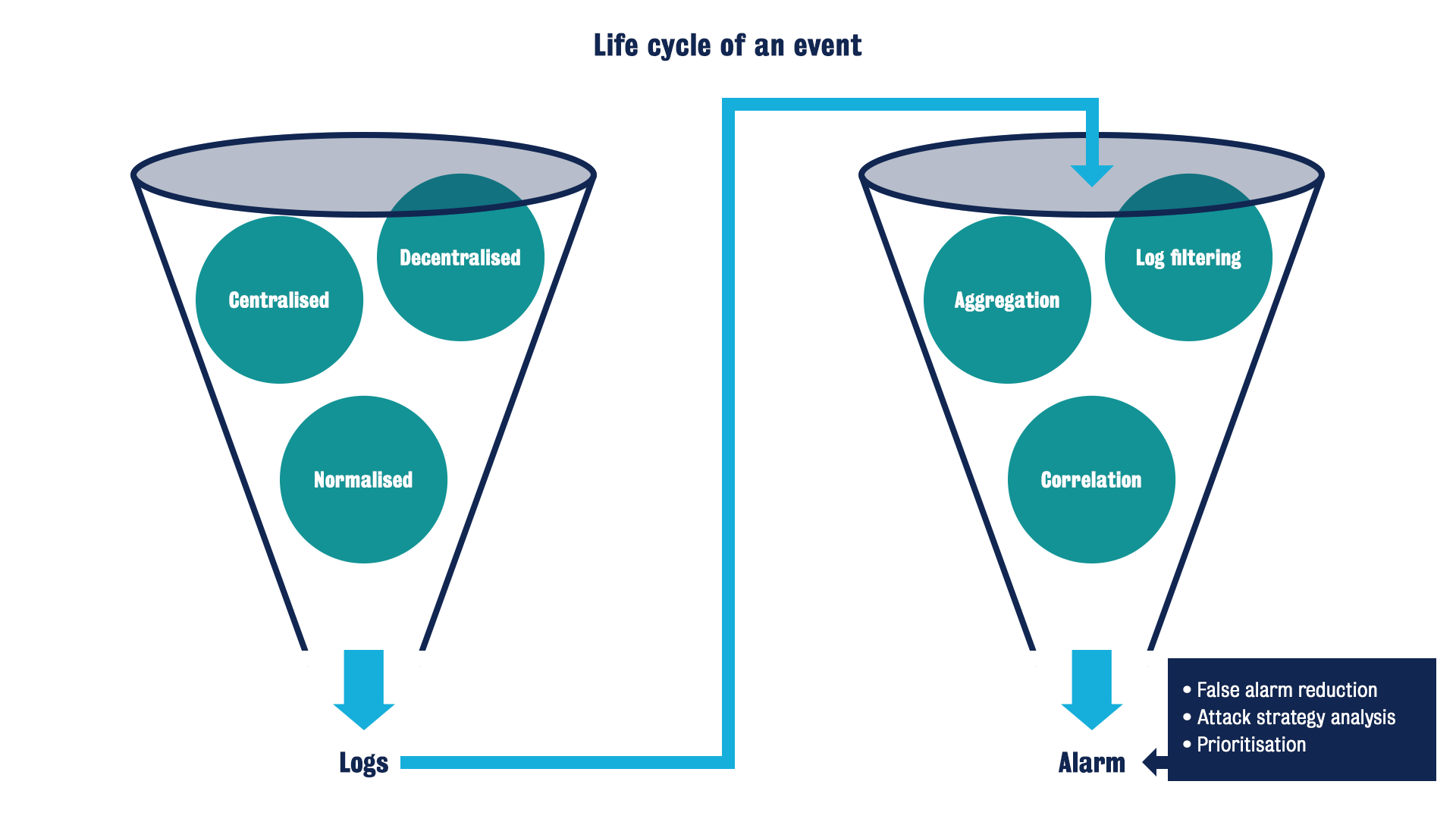
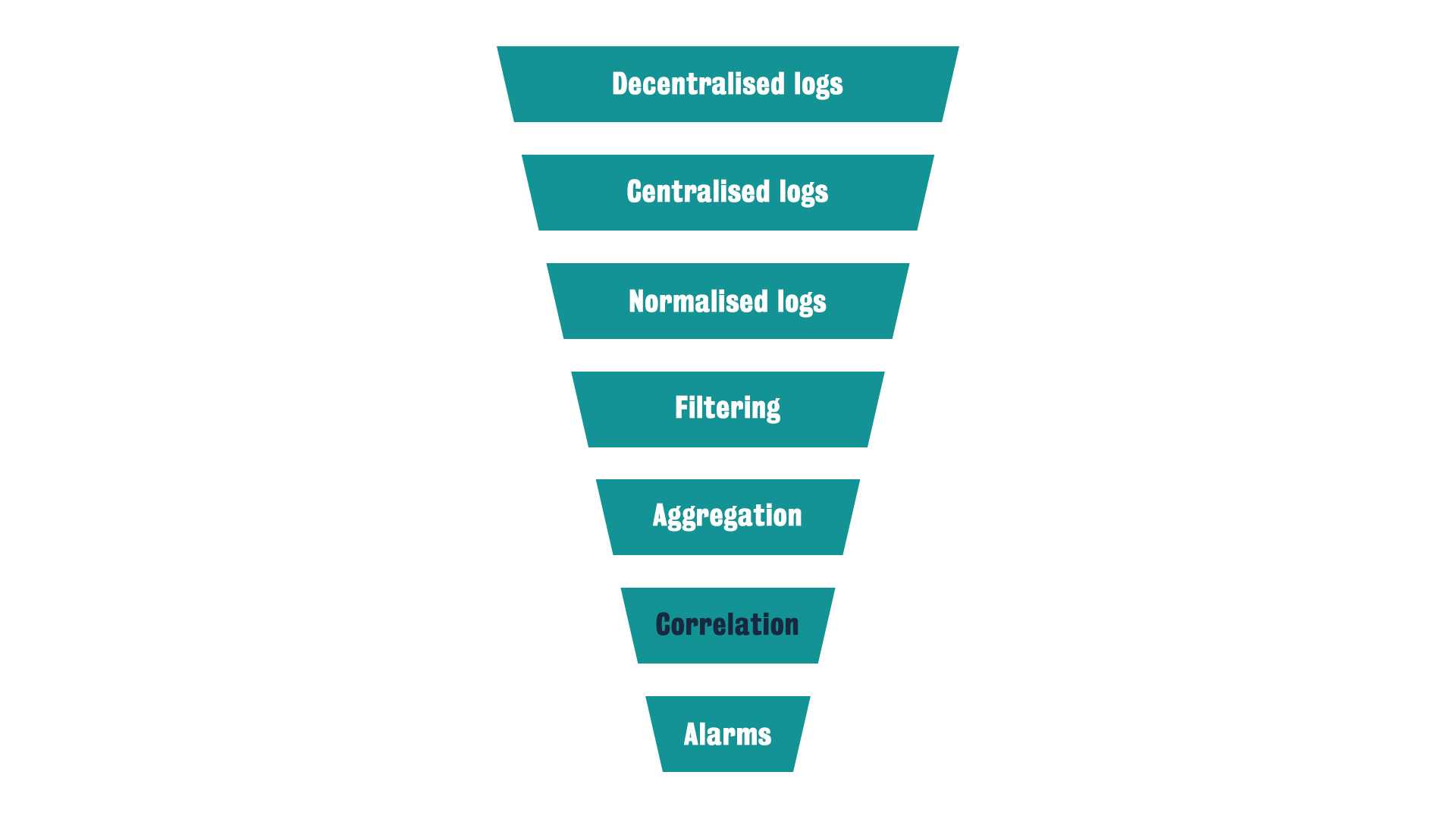
What is the lifecycle of events?
-
turn information from unstructured logs with low-level descriptions of the characteristics of events
-
into a high-level representation of actionable events, namely alarms
-
The first funnel filters
-
- decentralised logs into centralised logs
-
- then turn into normalised logs
-
- then into the second funnel
-
-
The second funnel produces alarms through
- log filtering
- aggregation,
- correlation
- finally trigger the alarms
-
Final alarms supported by
- false alarm reduction
- attack strategy analysis
- prioritisation
What are Alarms?
- Alarms
- are meant to be reported to humans
- alarms help security operator analyse the strategy of an attack and prioritise responses.
What is normalisation of logs?
is the procedure in which
- all logs that are processed by an intrusion detection system
- are processed and stored in a common format
- and all relevant attributes of the event are identified and processed
What is event correlation?
Event correlation brings a higher level of intelligence to the process
It teaches the system to consider various conditions before trigger the alarm
What is the Security information management (SIM)?
The practice of collecting, monitoring and analysing security-related data from computer logs.
What is the Security information management system (SIMS)?
- It automates the collection of event log data from security devices
- It translates the logged data into correlated and simplified formats
- It has strong log management capabilities (compress logs for storing over long periods of time)
What is the Security event management (SEM) systems?
It provides strong:
- event management
- real time threat analysis
- visualisation
- ticketing
- incident response
- and security operations
Based on enterprise SQL databases
Not ideal for log management and long-term storage of excessive amounts of logs (poor at log compression)
What is the (OSSIM)?
How Open Source Security Information Management (OSSIM) evaluates the risks?
Risk = (Asset * Priority * Reliability) /25
- Asset
- is the quantitative measure of the importance
- and/or a notion of how vulnerable a given asset is
- Priority
- is the threat or impact of the attack
- Reliability
- is the probability that a given set of events will actually be an attack
- Asset - 0 - 5
- Priority - 0 - 5
- Reliability - 0 - 10
- 0 - 2 = Low
- 3 - 4 = Medium
- 5 - 6 = Medium-high
- 7 - 8 = High
- 9 - 10 = Very high
How forensics cooperate with SIEM?
forensic investigator would collect the evidence from the source, the native logs.
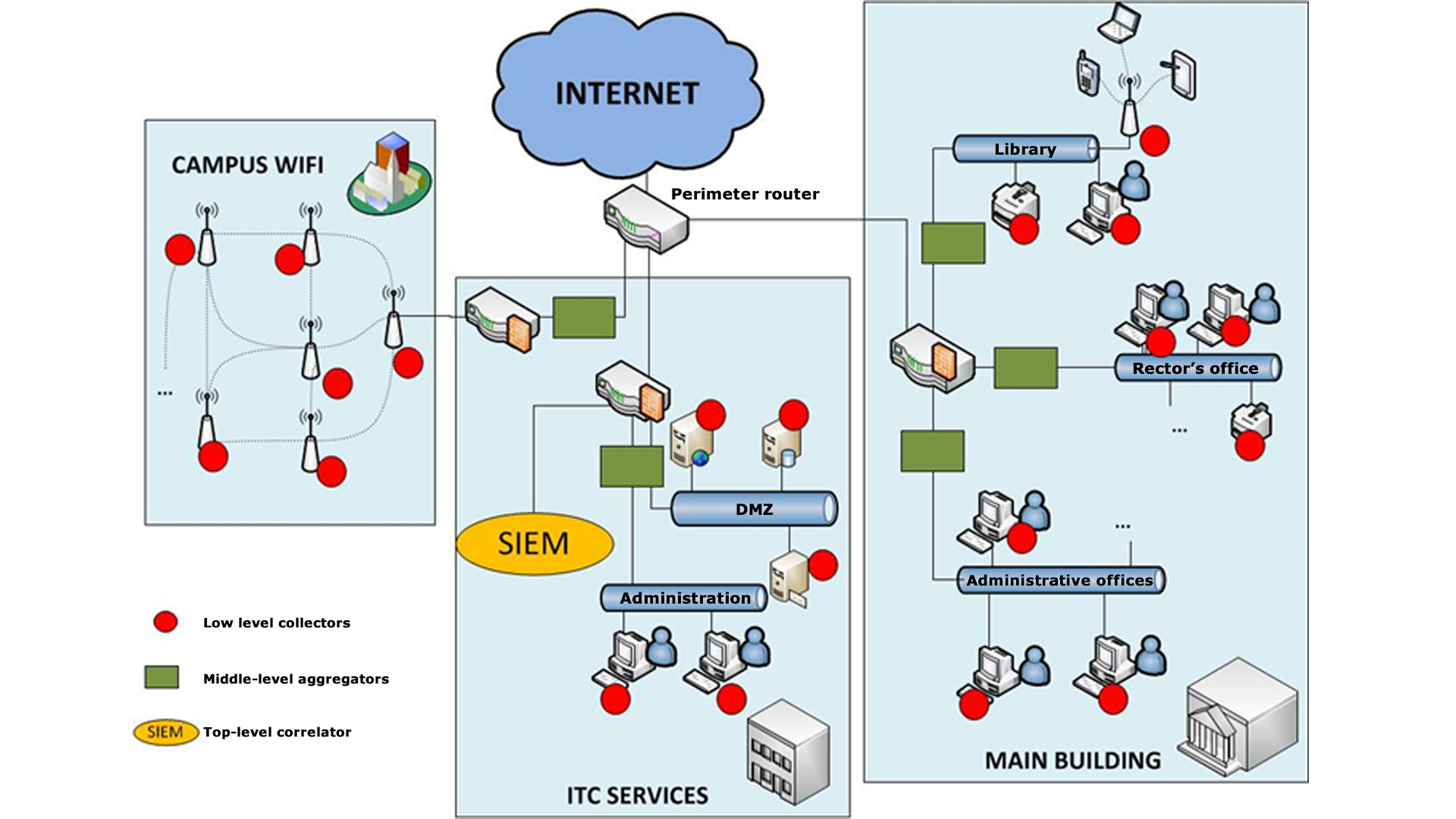
What is the Sensing strategies?
It defines how the SIEM is deployed.
It details:
-
Where to place the different sensors
-
how these sensors are interconnected
-
what the security measures are
-
who the people in charge of each sensor are
-
- collectors,
- normalisers
- aggregators
- Intrusion Detection Systems and correlation and report engines