CFC Week 3: Malware uses and monetisation
Learning outcomes
- Explain the different monetisation strategies.
- Discuss the other ways malware is used, apart from monetisation.
- Explain how cybercrime is a commodity and how it is supported by an underground economy.
What is the information-stealing malware?
Information-stealing malware monitors its victims to collect usernames, passwords and financial information
What is two-factor authentication?
- what you know (password)
- what you have (mobile phone for code)
- what you are (fingerprint, face, retina)
What is man-in-the-browser attack?
Man-in-the-browser attacks changes the browser window and makes users think that they are performing a legitimate transaction when they are sending money to the attacker instead.
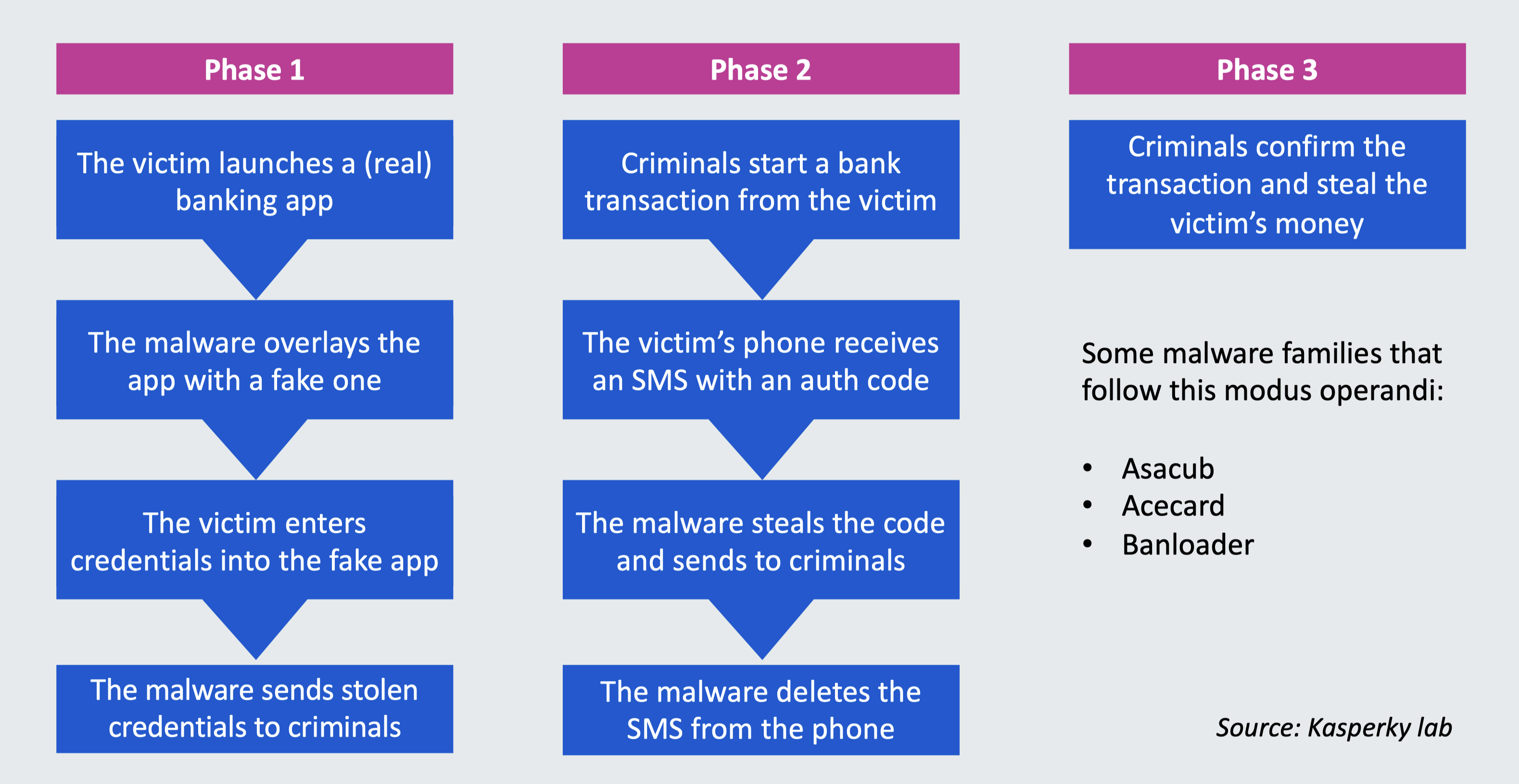
Describe operations of a mobile banking trojans
What is Ransomware
Cybercriminals encrypt user’s files and ask for a ransom to decrypt them again
What is fake antivirus?
- lure user to pay the money and download fake antivirus.
- The fake antivirus doesn’t to anything, but perform malicious activities itself
What is pay-per-installs scheme
rent botnets for other cybercriminals for installing malware
What is DDoS as a service
- Types
use servers: higher bandwidth
use infected computers: cheaper
- Services
damage their competitor
stress-testing services
Mining bitcoin
use infected computers to mine bitcoin, set up botnets
Ways of using malware to make money
- Man-in-the-browser attacks
- Financial malware
- Ransomware
- Fake anti-virus
- DDoS as a service
- Mining bitcoin
How underground communities avoid lemon market?
- self-policing
- scrutinise newly listed products and services
- interview people who want to join
- require recommendations from joined members to join
- escrow system
- payments first made to the administrator
- forwarded to seller after authenticity has been confirmed
How cybercrime supported by an underground economy?
-
CAPTCHA-solving service : automated software solver or human manually solve the CAPTCHAs
-
Phone vertification abuse : - use Voice over IP (VoIP) numbers
-
purchase SIM cards in developing countries (cheap)
-
use SMS-vertification as a service
-
-
Fake social media accounts : - automatically create accounts and followers
-
Proxy : is a server that relays connections for a host, which hide the location and circumvent censorship
-
Exploit kits : automate the exploitation of vulnerabilities
-
Payment : - find banks willing to process criminal payment (high transaction fees)
- use cryptocurrency